Employment Formats in Norway
.png)
Overview of the formats
Understanding employment contracts and formats of employment in Norway is crucial for both employers and employees. Norwegian employment contracts are regulated to ensure fair working conditions, social security, and clear employment relationships. This guide provides an overview of the different types of employment, requirements for employment contracts, working hours, and employee rights in Norway. Our conpany can assist according to your needs.
%20-%20visual%20selection%20(1).png)
Employment Contract in Norway
An employment contract in Norway is a legally binding agreement between the employer and the employee. The Norwegian Working Environment Act requires a written employment contract for all employment relationships, ensuring clarity on terms such as working hours, and place of work, the Norwegian employment contracts must include.
Employment Contract in Norway
In Norway, an employment contract is a legally binding agreement between the employer and the employee. The Norwegian Working Environment Act mandates that all employment relationships must be formalized through a written employment contract. This ensures clarity on key terms, including working hours, job description, place of work, and other critical employment details.
Requirements for Employment Contracts
Norwegian employment contracts must clearly outline essential aspects of the employment relationship. This includes a detailed job description and duties, specific working hours and weekly working hours, and the designated place of work. The contract should state the duration of employment, specifying whether it is a permanent or fixed-term position. If applicable, the contract should also mention any trial or probationary period. Social security contributions and employee benefits must be clearly defined to ensure transparency.
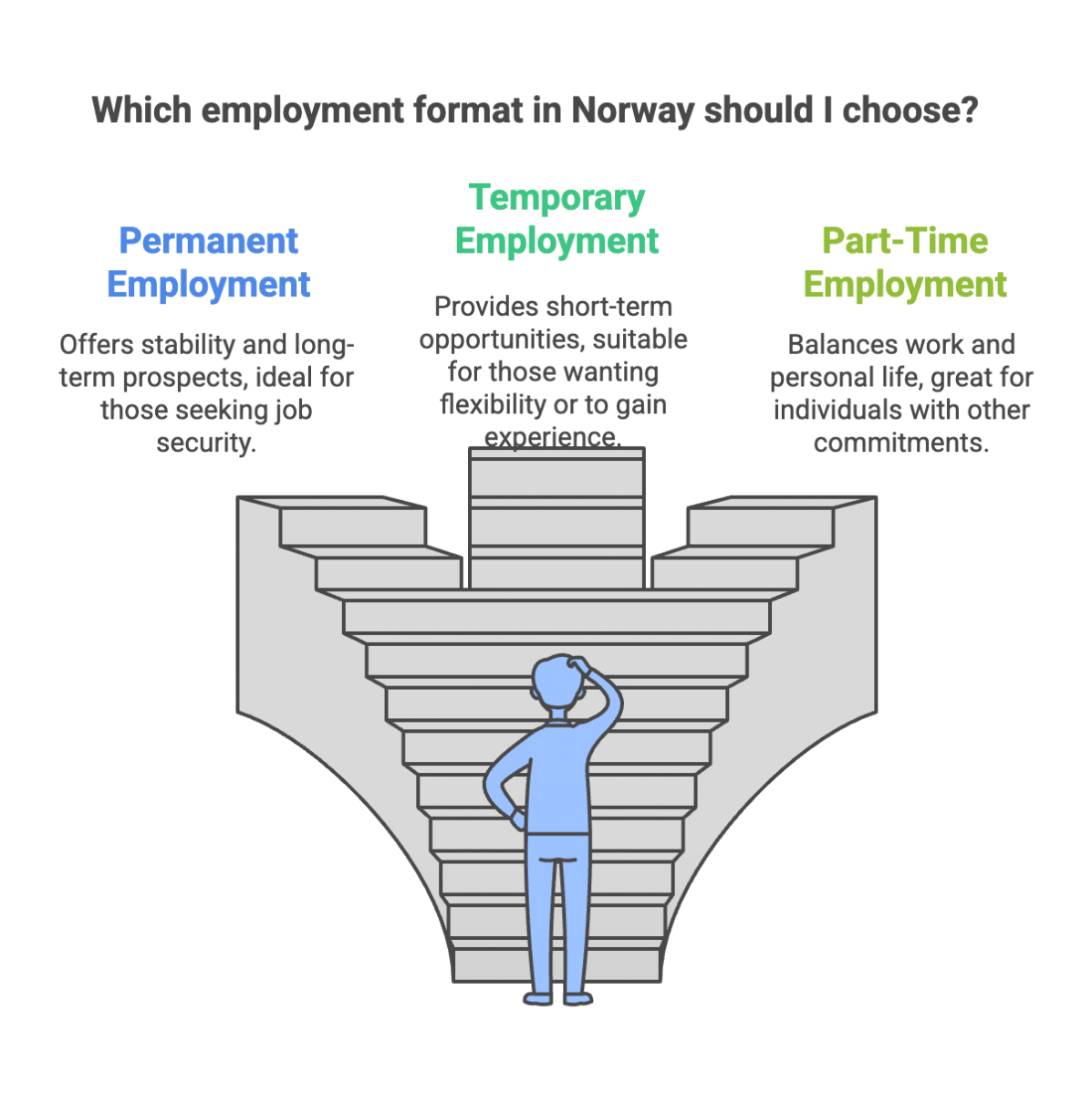
Types of Employment
There are several common types of employment contracts in Norway. Permanent employment is the most prevalent, offering job security and comprehensive benefits. Fixed-term employment is often used for temporary projects or seasonal work, but it requires specific legal justifications under Norwegian employment law. Temporary employment contracts are also common, typically utilized for substitute roles or specific tasks that require short-term staffing. Freelance contracts are another option, allowing independent contractors to work flexibly, though they do not receive the same benefits as regular employees.
.png)
Standard working hours in Norway are 37.5 hours per week, with daily working hours generally not exceeding 9 hours. Overtime work is regulated and must be compensated according to Norwegian labor laws. Remote work has become increasingly common, especially following the COVID-19 pandemic, offering employees more flexibility. Employees are also entitled to holiday leave, which includes holiday pay, ensuring a balanced work-life environment.
Employment Agreement and Working Environment
The employment agreement serves as the foundation of the working relationship, outlining all terms and conditions. It ensures that both parties comply with Norwegian labor laws and promotes a healthy working environment. The Norwegian Labour Inspection Authority is responsible for overseeing and enforcing these regulations, safeguarding employees’ rights and workplace standards.
Many employment contracts in Norway include a probationary period, typically lasting up to six months. This period allows both the employer and the employee to evaluate the suitability of the employment relationship. During the probationary period, the notice period for termination is usually shorter, providing flexibility for both parties.
Termination of Employment
Termination of employment in Norway must adhere to the guidelines set forth in the Norwegian Working Environment Act. Employees are entitled to a notice period based on their length of service, and employers must present valid reasons for termination. This legal framework ensures that employees are protected from unfair dismissal.
Social Security and Employee Rights
Employees in Norway benefit from a comprehensive social security system that covers healthcare, pensions, and unemployment benefits. Sick leave is well-compensated, and the country’s generous parental leave policies support work-life balance. These benefits contribute to the overall well-being and job satisfaction of employees.
Collective Agreements and Employment Laws
Collective agreements play a significant role in the Norwegian labor market, establishing industry-specific standards for wages, working hours, and other employment conditions. The Norwegian Labour Inspection Authority ensures that these agreements, along with national employment laws, are upheld to maintain fair labor practices.
Recent Trends and Statistics (2020-2024)
The Norwegian labor market has experienced notable changes between 2020 and 2024. The proportion of temporary employment fluctuated between 7.7% and 9.3%, reflecting shifts in market demands. Remote work saw a significant increase following the 2020 pandemic, becoming a staple in many industries. Average weekly working hours remained consistent at around 37.5 hours, maintaining the country’s emphasis on work-life balance. Sectors such as education, healthcare, and technology saw heightened demand for skilled labor, driving employment growth in these fields.
%20-%20visual%20selection.png)
Conclusion
Navigating the various contracts and formats of employment in Norway is essential for fostering positive and transparent employment relationships. Employers must ensure that their employment contracts comply with Norwegian labor laws, while employees should be aware of their rights and responsibilities. Whether seeking permanent employment, a fixed-term contract, or freelance opportunities, Norway offers a structured and equitable employment landscape. For more information on employment contracts in Norway or to explore new opportunities, contact RED. Recruitment today!

